CompView (technology for the model
create and control)
Overview
The technological scheme creation, edition and modeling on big volume of real data in
offline and online modes. It was created on Visual C++ 4,5,6 versions.
Technology description
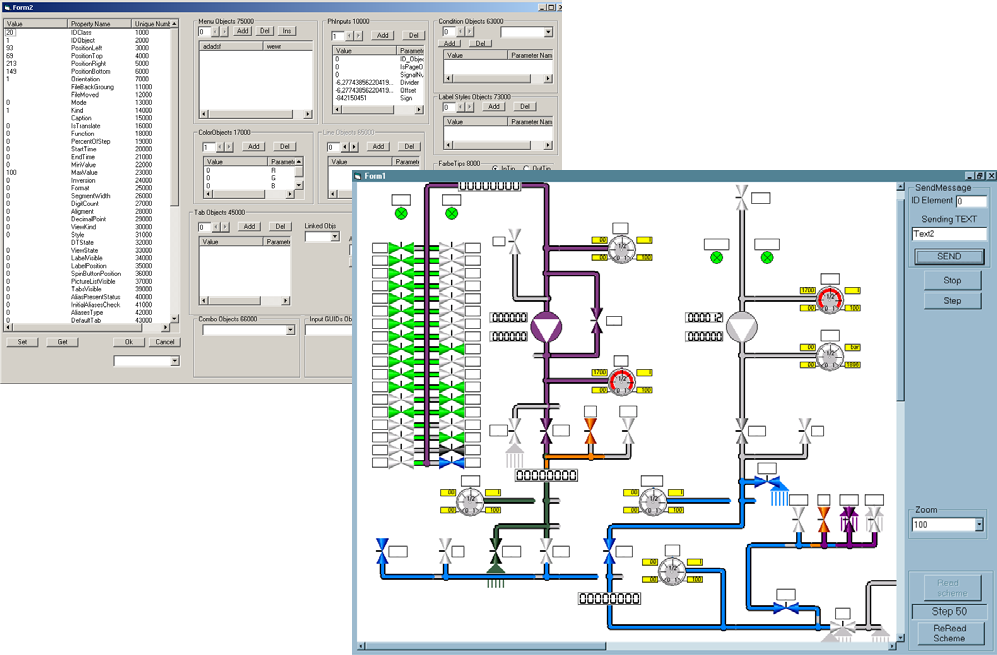
This is full closed and ready‐made programming technological cycle of scheme edition and
dynamical data visualization in real‐time mode. A lot of properties for each scheme object
are using.
Object Editor
The powerful build‐in editor of objects permits the almost of all modern existed editing features.
Wide area of applications:
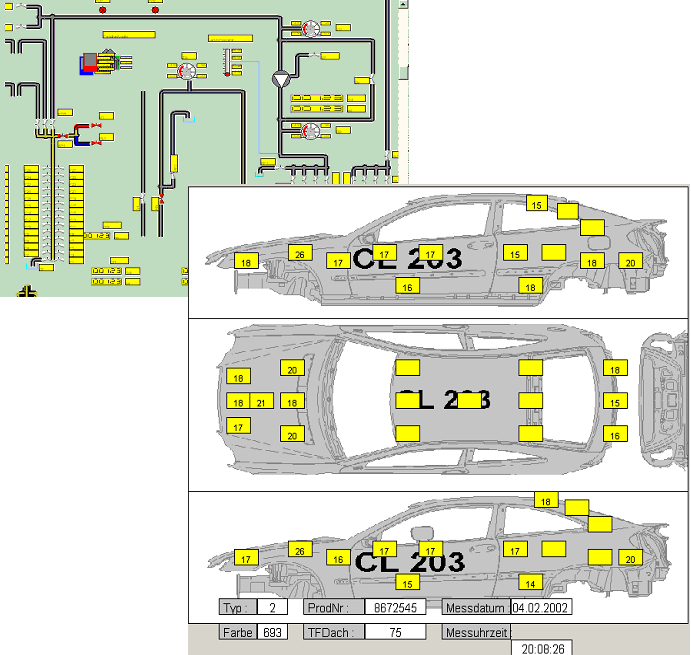
| For car building technology |
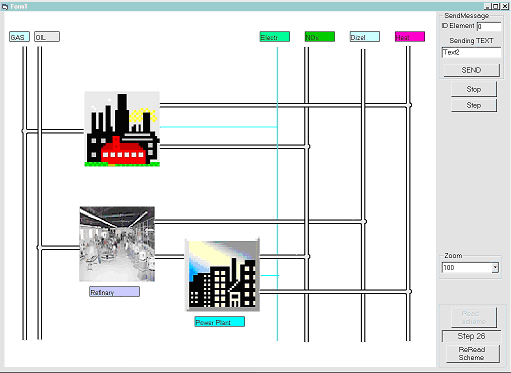
For energy-economy analysis of energy consumption |
 |

|
The technology permits:
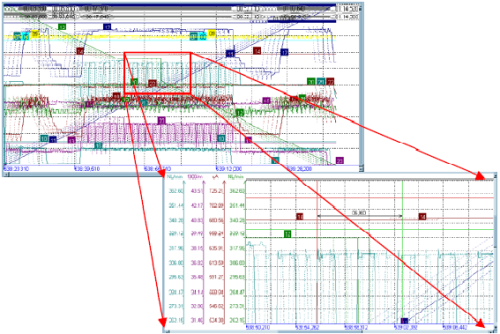
To visualize and compute of huge volume of data (more then 100 billions of values in several formats) with high performance. The special computing methods are using to improve performance;
 |
 |
| To zoom the data through computing zooming |
The selective visualization of data with special statistic methods |
PageView project
To do the special recompile of data; to make the reverse data depends; to do the flexible tuning to data formats. To use a lot of data formats such as ODBC, DAO, ADO, XML and more; to make multi‐channel data access.
Computational FD/H&MT:models, methods, and software
Application software is a powerful forecasting system:
- object‐oriented(to users)
- with a graphical user interface (GUI)
- with modern mathematical models
- with approved reference information databases
|
 |
Application software examples
| Problems |
Software |
| Fluid dynamics, Heat & Mass Transfer |
AnsysFluent, OpenFoam, Code Saturn, IES VE |
| Energy Saving |
IES VE, Energy Plus, ESP‐r, VABI Elements |
| Engineering Equipment Design |
MatLAB Simulink, TRNSYS, IES VE, Energy Plus |
| Acoustics |
DIRAC, Ansys Fluent |
| Heat&MassTransfer in Solids, Structural Mechanics |
Comsol, BSim, Delphin5, HAMLab |
|
Computational FD/H&MT:our solved tasks
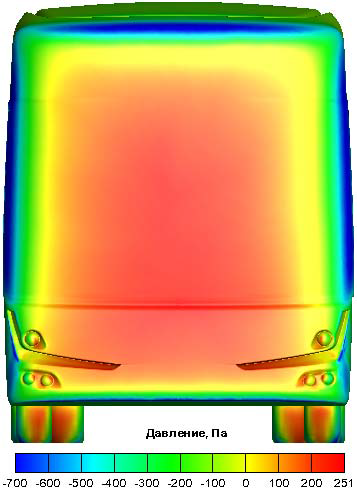
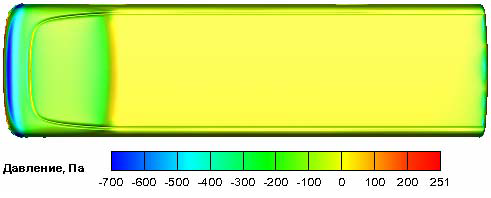
Bus aerodynamics simulation

|
 |
- 3D problem using the CAD modelclose to a real bus
- Steady RANS equations,SST–k–ω turbulence model,upwind scheme,SIMPLEС algorithm
- Used software: AnsysFluent14.5
|
|

|
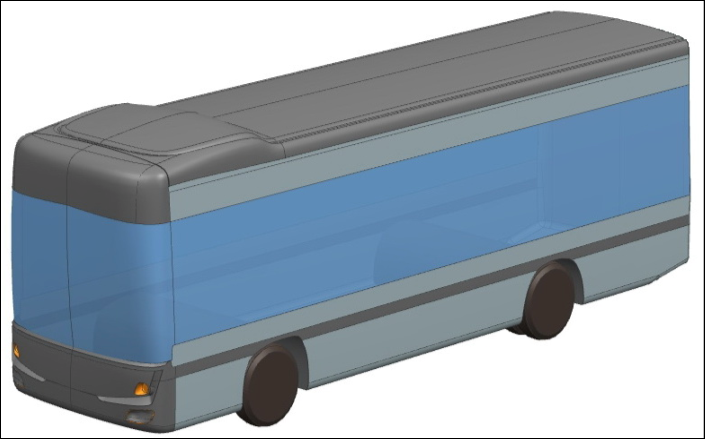
Pressure distribution |
 |
 |
|
Fp, N |
Ff, N |
Fx, N |
Cp |
Cn |
Cx |
| Rear wheels |
69.70 |
3.75 |
73.45 |
0.024 |
0.0013 |
0.0253 |
| Front wheels |
9.10 |
2.00 |
11.10 |
0.003 |
0.0007 |
0.0037 |
| Bus surface |
1058.4 |
86.3 |
1144.7 |
0.361 |
0.0294 |
0.3904 |
| Total |
1137.20 |
92.05 |
1229.25 |
0.3880 |
0.0314 |
0.4194 |
|
Pressure forceFp, friction force Ff, total force FX, pressure coefficient Сp, friction coefficient Сf, and total coefficient СX at a velocityof 90 km/hr
|
Bus aerodynamics simulation
|
 |
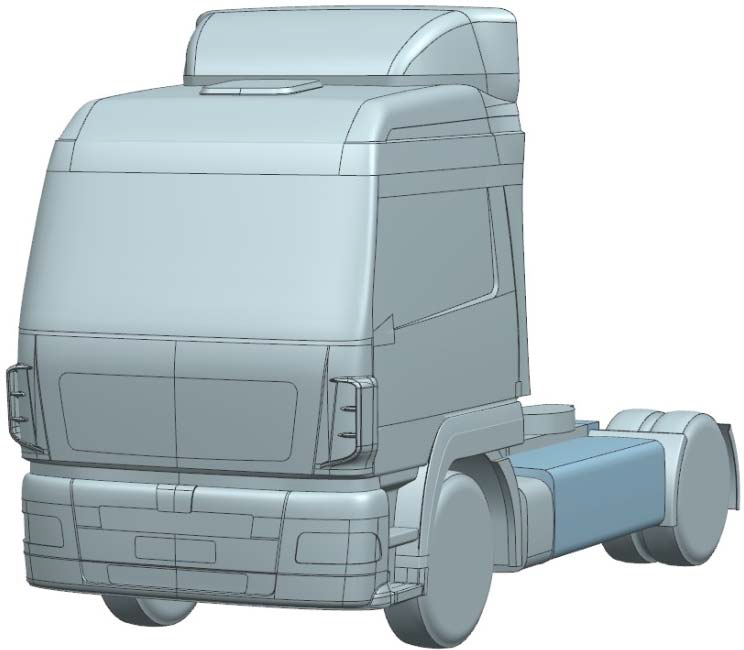
- 3D problem using the CAD modelclose to a real truck
- Steady RANS equations,SST–k–ω turbulence model,upwind scheme,SIMPLEС algorithm
- Used software: AnsysFluent14.5
|
 |
 |
 |
Aerodynamic drag force and drag coefficient of serial and new truck cabins
|
Ft, N |
Сt |
| Serialcabin (S=8.642 m2) |
499.5 |
0.151 |
| New cabin (S=8.642 m2) |
531.4 |
0.163 |
Aerodynamic forces for new cabin
| cabin element |
Fp, N |
Ff, N |
Fx, N |
Cp |
Cn |
Cx |
| deflector |
‐37.5 |
0.4 |
‐37.1 |
‐0.0108 |
0.00012 |
‐0.0107 |
| radiator grille |
227.3 |
0 |
227.3 |
0.0663 |
0 |
0.0663 |
| rearview mirrors |
59.6 |
1.2 |
60.8 |
0.017 |
0.00035 |
0.0173 |
| bumper |
267.1 |
1.7 |
268.8 |
0.0779 |
0.00049 |
0.0784 |
| total cabin |
684.8 |
19.0 |
703.8 |
0.1997 |
0.00553 |
0.205 |
|
|
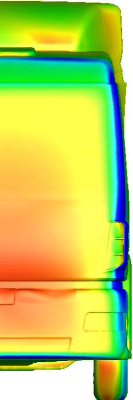
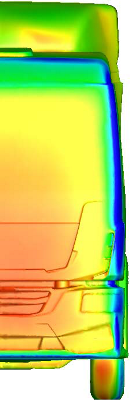
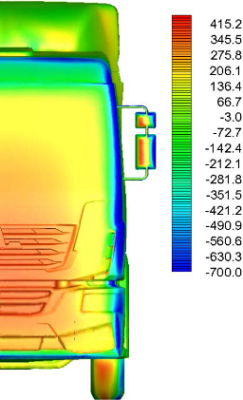
Pressure distribution at the front surface
of serial and new cabins (w/o and with rearview
mirrors)
|
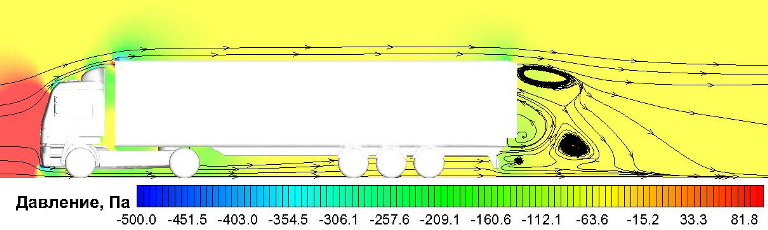
Truck aerodynamics simulation: rear flap influence
Rear flaps decrease a truck drag by 6.4% |
|
Fp, N |
Ff, N |
Fx, N |
Cp |
Cn |
Cx |
| Truck w/o flaps(S=10.62 m2) |
2337.6 |
127.2 |
2464.8 |
0.575 |
0.031 |
0.606 |
| Truck with flaps(S=10.81 m2) |
2215.1 |
133.3 |
2348.4 |
0.535 |
0.032 |
0.567 |
|
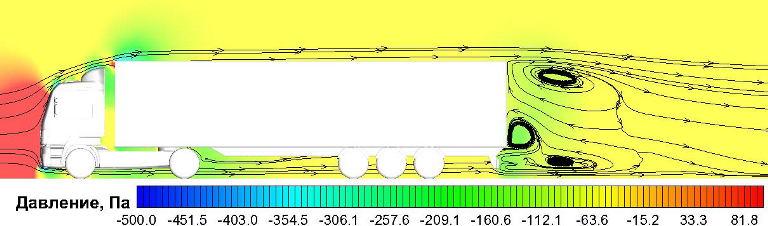 |
Pressure distribution
and streamlines |
 |
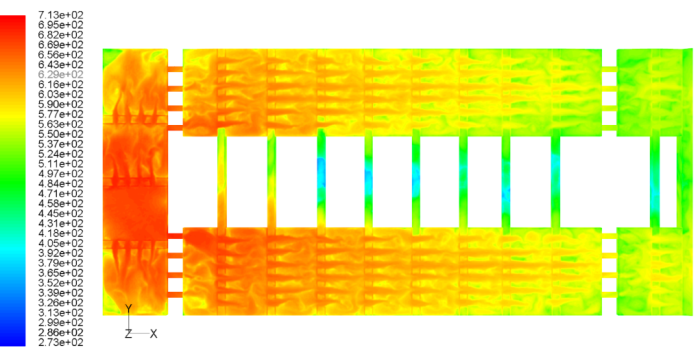
Heating a truck body by exhaust gases
 |
- Conjugate problem of heat transfer from exhaust gases to the truck body surface
- Used software: AnsysFluent 14.5
|
| Input gas temperature–713K, Gas flowrate–1700kg/hr.
Gas temperature at the heating system exit of an empty truck body–300 ° C;
Pressure drop–30 kPa;
Mechanical power loss –19.2kW |
 |